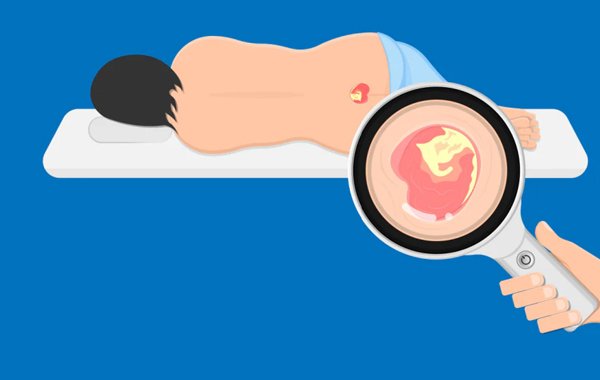
Spinal cord injury patients are at a higher risk for developing bed sores, also known as pressure ulcers or pressure sores, due to decreased mobility, sensation, and blood flow. The main cause of bed sores in SCI patients is prolonged pressure on the skin and soft tissues, which leads to tissue damage and skin breakdown. Here are some specific causes of bed sores in SCI patients: Immobility: Individuals with SCI often have limited mobility, which can cause pressure on specific areas of the body and increase the risk of developing bed sores. This is especially true for those who are unable to shift their weight or change positions independently. Lack of sensation: SCI patients may have decreased or absent sensation in certain areas of the body, making it difficult to detect early signs of skin breakdown. This can lead to delayed treatment and increased risk of developing bed sores. Incontinence: SCI patients may experience bowel or bladder incontinence, which can lead to skin irritation, maceration, and increased risk of developing bed sores. Shearing forces: SCI patients who are repositioned or moved frequently may experience shearing forces on the skin, which can lead to tissue damage and increased risk of developing bed sores. Poor nutrition: SCI patients may have difficulty maintaining a healthy diet, which can lead to malnutrition and weakened skin, increasing the risk of developing bed sores. Certain medical conditions: SCI patients with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or circulatory problems, may be at higher risk of developing bed sores due to impaired blood flow to the skin and soft tissues. Stages of Bed sores In individuals with SCI, pressure sores often occur in areas where there is prolonged pressure, such as the sacrum, buttocks, and heels. It is important to catch pressure sores in the early stages to prevent progression to more severe stages. There are four stages of pressure sores, each with increasing severity: Stage 1: This is the mildest stage of pressure sores, where the skin may appear red, but it is not broken. The affected area may feel warm or spongy to the touch, and the person may experience itching or pain. Stage 2: In this stage, the skin is broken and there may be a shallow open wound or blister. The area around the sore may be red and inflamed, and there may be some drainage or pus. Stage 3: At this stage, the sore has extended through the skin and into the underlying tissues, such as muscle or fat. The wound may be deeper and appear as a crater-like hole, and there may be signs of infection such as redness, warmth, and pus. Stage 4: This is the most severe stage of pressure sores, where the wound has become very deep, extending into the muscle, bone, or joint. There may be necrosis or dead tissue, and the wound may have a foul odor. Infection is very likely at this stage, and there is a risk of complications such as sepsis. Prevention of Bed Sores Preventing bed sores is very important for individuals with spinal cord injury, as it has a great impact on the patient’s rehabilitation and also they are painful and may increase the risk of infection, which can be especially dangerous for individuals with spinal cord injuries.Here are some specific prevention strategies for SCI patients: Regular repositioning: SCI patients should be repositioned at least every two hours to relieve pressure on the skin. This can be done manually by a caregiver or with the help of specialized equipment, such as a tilt table or turning frame. Pressure relief devices: There are various pressure relief devices that can be used to help prevent bed sores in SCI patients, such as cushions, mattresses, and overlays. These devices work by distributing pressure over a larger surface area and reducing the risk of skin breakdown. Skin care: Keeping the skin clean and dry is important for preventing bed sores. SCI patients should be washed with mild soap and water, and moisturizers can be used to keep the skin hydrated. Any areas of redness or irritation should be addressed promptly. Nutrition: A healthy diet with adequate protein intake is important for promoting skin health and preventing bed sores. SCI patients may also benefit from nutritional supplements, such as vitamins and minerals. Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve circulation and prevent bed sores. SCI patients should work with a physical therapist to develop an exercise program that is safe and appropriate for their level of injury. Manage moisture: Excessive moisture on the skin can increase the risk of developing bed sores. Incontinence should be managed promptly, and moisture-wicking fabrics can be used to keep the skin dry. Regular skin checks: SCI patients and caregivers should regularly check the skin for any signs of redness, irritation, or pressure sores. Early detection and treatment can prevent bed sores from developing or worsening. So, it is very important to seek medical advice as soon as possible to prevent progression of bed sores to more severe stages, which can result in complications such as infection and sepsis. By Virendra Vikram Singh(PT)